Unit 4 - Cybersecurity
Principles of Cybersecurity
Learning Objectives
Understand basic cybersecurity concepts
- The CIA triad
- People, processes, and technologies that relate to CIA
Understand the differences between a threat and a vulnerability
- Threats, vulnerabilities, and exploits
- How attackers exploit infected computers
- Best practices for threat prevention
Understand fundamental user security processes
- Identification, Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
- Proper password configuration
Section 1
The CIA Triad
3 Goals of information security:
Maintain information confidentiality
Making sure only approved users have access to data
Maintain information integrity
Data Integrity: assurance that information has not been tampered with or corrupted between the source and the end user
Source Integrity: assurance that the sender of the information is who it is supposed to be
- Maintain information availability
Ensuring data is accessible by approved users when needed
The CIA Triad: Tech Tools of the Trade
Confidentiality
Encryption
Passwords, encryption keys
User access control
- Controlling which users have access to networks and what level of access each user has
Integrity
Encryption
User access control
File permissions
- Customizable settings that only allow certain users to view and edit files Version control systems/backups
Availability
Offsite data storage/backups
Redundant architecture (hardware and software)
Section 2
Threats and Vulnerabilities
Important Cybersecurity Definitions
Threat: An attacker or piece of malware that desires and/or is able to cause harm to a target
Vulnerability: Flaw in an environment that an attacker can use to harm the target
Exploit: The method by which an attacker can use a vulnerability
Risk: The potential that a threat will exploit a vulnerability
Risks: Probability and Impact
The risk of a cybersecurity attack depends on two factors
Probability
How much motivation does an attacker have to try to exploit my system?
How securely have I protected my system?
Impact
How damaging is a potential attack on my system?
Types of impact: Financial, Health and Safety, Personal, Service Interruption
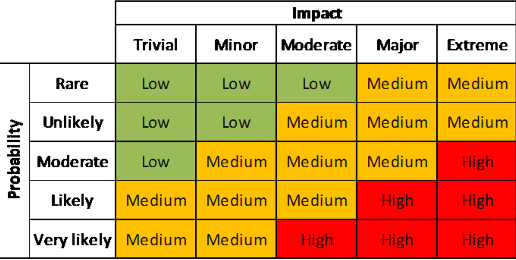
Risk Assessment: Target Breach
Case: Attackers breached Target’s network through a heating and air conditioning (HVAC) company and point-of-sale systems to steal 40 million credit card numbers
Likelihood: Likely
- Attackers knew that Target has a massive network with many potential holes and that they could gain a wealth of information
- Network was not fully secured; HVAC company had open access to it
Impact: Major
- Loss of financial information could have major impact on Target’s customers
- Breach was a huge embarrassment to Target and could have led to decrease in future sales
Section 3
Cyber Threats and Countermeasures
Physical Threats:
Dumpster Diving
- Thieves sift through garbage for receipts with credit card information, medical forms with social security numbers, or other documents with PII
Shoulder Surfing
- By looking over your shoulder as you type, thieves can glean your passwords, account information, and other sensitive information
Cyber Hygiene
Basic personal practices that keep computers and data safe
Lock your computer when in public areas
Shield your keyboard when you type passwords
Do not let strangers use your computer
Keep sensitive information in secure places
What are mobile devices?
A Mobile Device is a Portable or handheld devices that have data or can connect to another device that has data
Phones
Laptops
Tablets
Etc...
Social Engineering
- Social Engineering: Manipulating people into giving up personal information
Example:
M@ckelm0re: Yo man I got the illest sweaters yesterday
Ry@nLew1s: Really? What are we talkin? Wool? Pullover? Cardigan?
Ry@nLew1s: I got a dope cardigan last week. Only 99 cents.
M@ckelm0re: A couple of sick purple pullovers. Dont know if I need 2 tho….whats ur address? I will drop 1 in the mail for u.
Social Engineering Methods
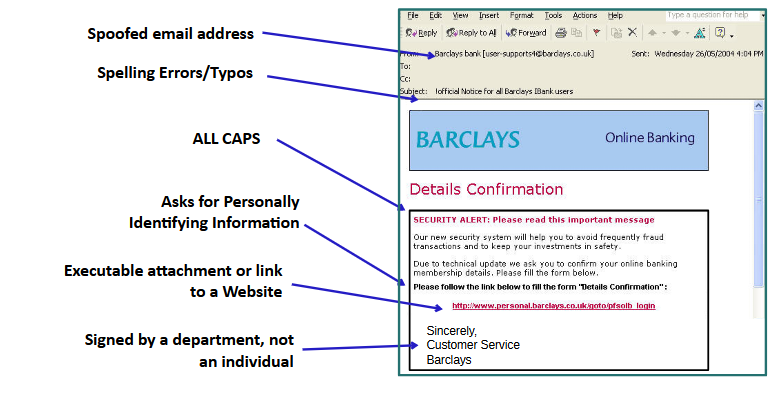
Phishing: fraud attempts perpetrated by random attackers against a wide number of users
Spear-phishing: fraud attempts targeted at specific people based on their membership or affiliation with a the spoofed group
- e.g. fraudulent emails sent to Microsoft employees aiming to steal Microsoft secrets
Vishing: Attempts to manipulate people into giving up PII over the phone
Smishing: Attempts to manipulate people into giving up PII by text message (SMS)
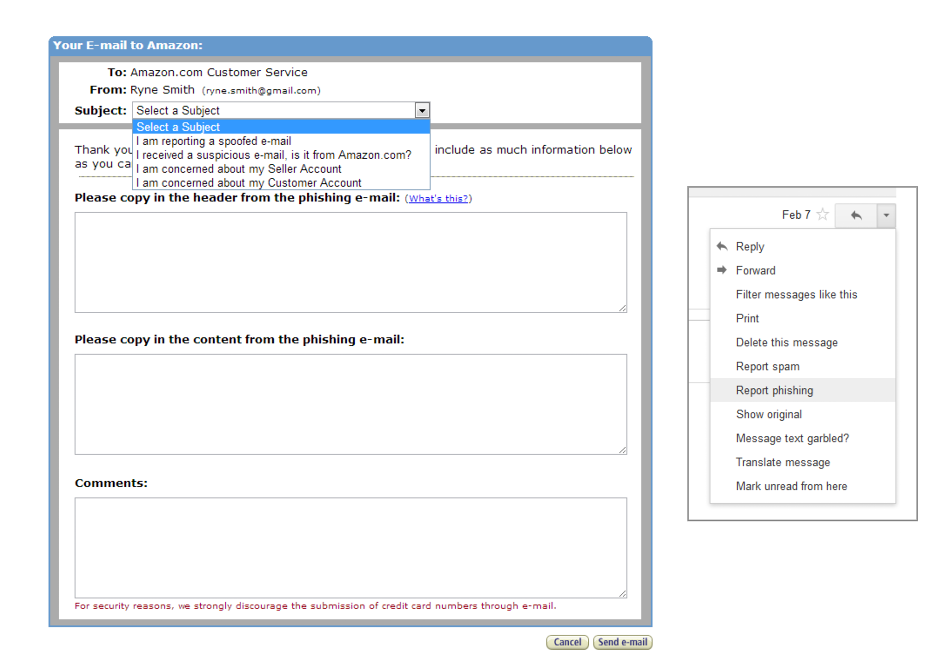
Reporting Email Scams
Report phishing attempts so other people aren’t victimized
Go to the legitimate website of the spoofed organization (not through a link in the email)
Follow the site’s procedure for reporting
Report the spoof to your email provider
Malware: What is it?
Malicious Software = Malware
Software designed and written to:
Steal information
Spy on users
Gain control of computers
Categorized by
How it spreads
What it does
Virus Variations
Viruses/Worms
Trojan Horses
Zombies and Botnets
Keyloggers
Backdoors
logic/Time Bombs
Spyware
Malware: Types & Terms
Viruses: Can infect and spread, but need human assistance
WormsWorms: Can infect and spread without human assistance
Trojan horse: Program with a hidden malicious function
Zombies (a.k.a. bots): compromised computers under the control of an attacker
Botnet: a collection of compromised computers (zombies) under the control of an attacker
Keylogger: Tracks users’ keystrokes, obtains passwords and other personal information
Backdoor: An entry point into a program without all the normal, built-in security checks
Logic/time bomb: Malware designed to lie dormant until a specific logical condition is met
Spyware: Collects information about you, without your knowledge or consent
Anti-malware Software

Section 3
Basic Cybersecurity Techniques
Basic Cybersecurity Techniques
Identification: Providing user identity to a system
Authentication: Verifying the user’s identity
Authorization: Determining whether a user is allowed to access certain resources
Accountability: Holding users responsible for their actions on a system
Identification and Authentication
Uses encryption to ensure that a user is who they say they are
Methods:
Passwords
Physical “keys” (key chains, swipe cards)
Biometrics (fingerprints, retina scanning)
Threats:
-Brute force cracking
Test every possible combination of letters, numbers, and characters until the password is found
-Dictionary cracking
Test words and combinations of words found in the dictionary or from a slightly shorter list of words known to be commonly used in passwords
Authorization
Uses tools to control access to a resource
Methods:
File permissions
Account management
Sharing settings
Threats:
Insider Threats
- Disgruntled or inexperienced employees that have high-level access may cause intentional or accidental harm to a system
Elevation of privilege
- Attacker is able to enter the system as a low-level user, but is able to attain high-level access
Methods covered in detail in Units 7 and 8
Accountability
Holds users responsible for their actions on a system
Methods:
System monitoring
Audit logs
Threats:
Denial of Service
- Attack overwhelms audit logs with excessive or very large log entries, causing the system to run slowly or not at all
Disclosure of confidential information
- Attacker is able to gather confidential or personally identifiable information from log files
Methods covered in detail in Unit 8
Authentication: Building Strong Passwords

Passwords - Complex
Passwords of 8 characters consisting of
Numbers only: 100 million Cracked under one second
+Lower case: 2.8 trillion Cracked under eleven minutes
+Upper case: 210 trillion Cracked under fifteen hours
+Symbols: 7.2 quadrillion Cracked under three weeks
Always use at least 3 of the following:
Numbers
Lower case letters
Upper case letters
Symbols (% # * & ! : { “ > |)

Passwords - Lengthy
Brute force attacks can run 4 billion calculations per second
-
Six or Fewer CharactersCracked within three minutes-
Seven CharactersCracked within five hours-
Eight CharactersCracked within three weeks-Nine Characters Cracked within five years
-Ten Characters Cracked within 526 years
Always use at least 8 characters

Passwords - Only Yours
Do not share your password with ANYONE
Passwords - Unique
Any of the top 10,000 passwords will be broken immediately
91% of people have one of the 1,000 most popular passwords
Almost half of all people use one of the 100 most popular
- password
- 123456
- 12345678
- abc123
- qwerty
- monkey

Passwords - Different
Use different passwords for each login (e.g. Gmail and Facebook)

Passwords - Short Term
The longer you keep a password the longer attackers have to try and crack it
Changing your passwords regularly can help foil cracking attempts as they happen
It’s best to change your passwords at least every few months
Passwords NOT Simple
Do not use dictionary words
- Fend off dictionary cracking attacks by using passphrases
Passwords - NOT User ID
User ID is publicly available
Using it as a password = Giving it away
Passwords - NOT Name
Do not use any personal info – can be easily found by other means
- Name
- Birthday
- Pet’s Name
- Mother’s Maiden Name
- Hometown
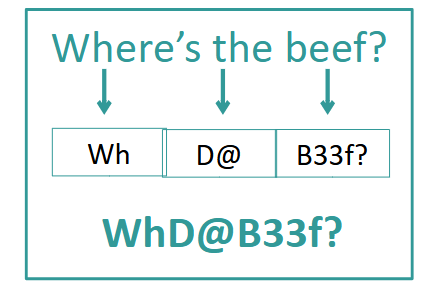
Old Gmail Password: Ronald123!GMA New Password: WhD@B33f?GMA
Old Facebook Password: Ronald1234FAC New Password: WhD@B33f?FAC
Building Strong Passwords
